Do you know that the average cost of phishing attacks costing a mid-size company $1.6 million? So, this can be a really expensive cost for your company if you don’t take the necessary steps to protect against a potential attack.
Here I would like to mention some necessary steps you can take to protect your company from phishing attacks.
Who Are Phishers and What They Want from You?
Phishers are persons or organizations who want to take some of your business or personal information and use it for themselves. Since 1996 phishers have done significantly increasing the array of attacks to systems to fool the victims and convey confidential and personal data. Even after so many years, phishing attacks and scams are still profitable for the professionals who run them.
Phishing attacks rely on a combination of technical and social hacking fraud. In most cases, the victim must be persuaded by the phisher to perform a series of actions that will ensure access to confidential information. Channels of communication such as email, web pages, instant messages are very popular in all cases, and phishers must play the role of a trusted source to enable the victim to believe.
While phishers create more sophisticated attacks, businesses continue to fail to protect their personal data and the data of their customers. Customers are becoming wary of “official” emails and they are putting the integrity of the websites that you need to connect questionable while confidence begins to lose.
Many different governments and industrial groups fight to prevent spam, organizations meantime take a proactive stance in the fight against the threat of phishing. By understanding the tools and techniques used by professional phishers, analyzing the mistakes in their security perimeter or application, organizations can prevent many of the famous and successful phishing attacks.
What Can You Do to Protect Your Small Business from Phishing Attackers?
As an entrepreneur, you need to learn more about technologies, techniques and local safety flaws that phishers exploit to carry out attacks to protect yourself from future attacks. With this information, organizations and customers can protect themselves from a next phishing scam to get to their inbox. In most of the cases, you will need some anti-phishing training to prepare yourself and your company to avoid phishing attacks. You can click here to test and reinforce your employees’ ability to combat phishing attacks.
The term phishing involves not only obtaining a user account information but also includes access to personal and financial data. Initially tricked users into replying to an email for passwords and credit cards, now spread to fake websites, install Trojan software, key-loggers and screen captures, all delivered via any electronic communication channel. The attackers are driven by the idea of making a lot of money for very little work. All that needs to be done is to create a new bank account, whereby the funds are received on the account and then sent that money with an international payment slip, which takes its commission and sometimes non-classical money laundering technique.
To further help protect your company’s private data, consider this Trailants preventing and training phishing attacks guide which will keep your organization safe.
Phishing Attacks Methods and Channels Used
Communication channels such as email, web pages, and instant messaging are very popular among phisher attackers today. In all cases, the phisher must mimic a trusted source (such as a service to help their bank, automatic messages from their favorite online retailers, etc.) for the victim to believe. Here is an email I get from false “Apple,” who ask to update my payment information.
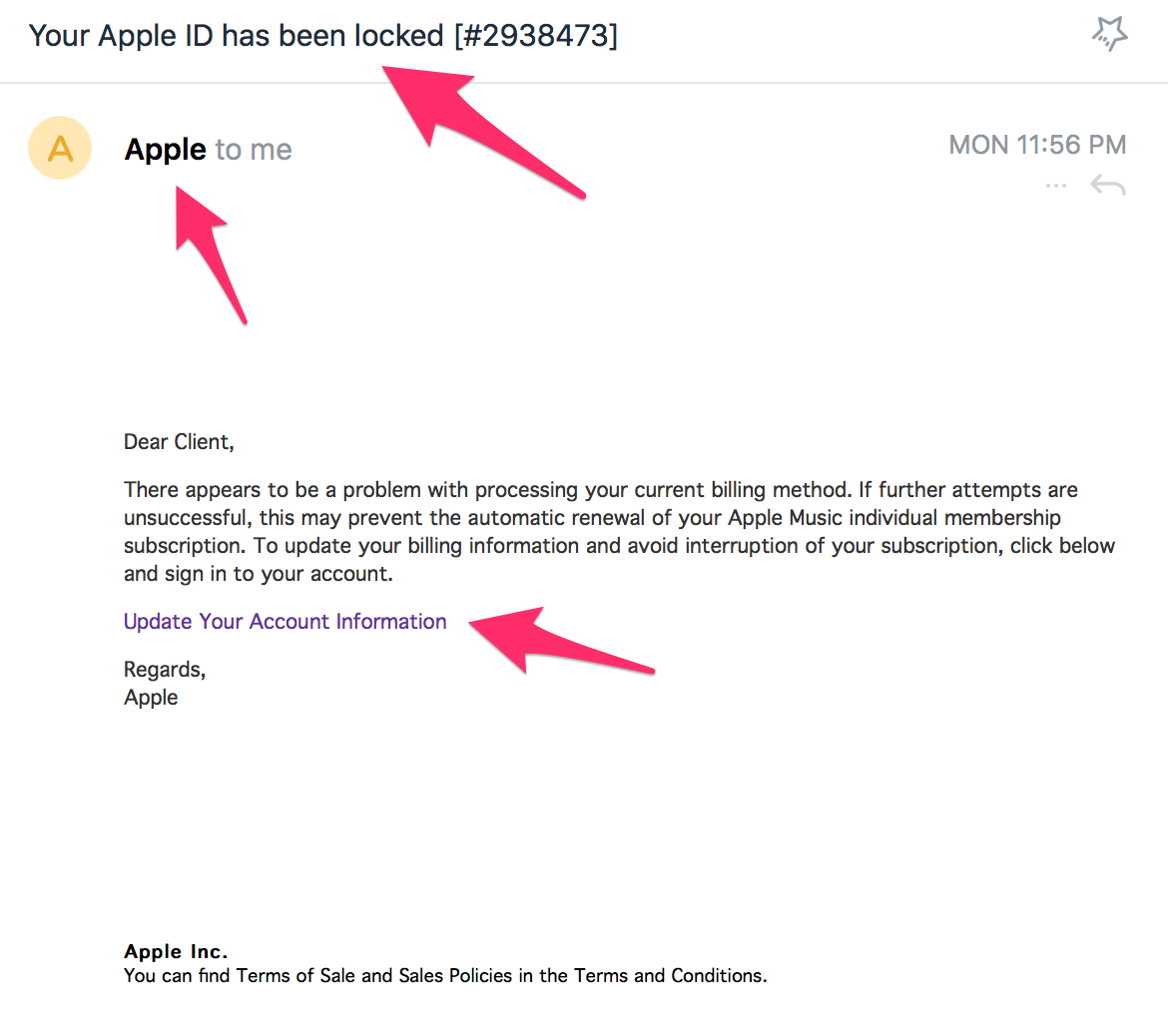
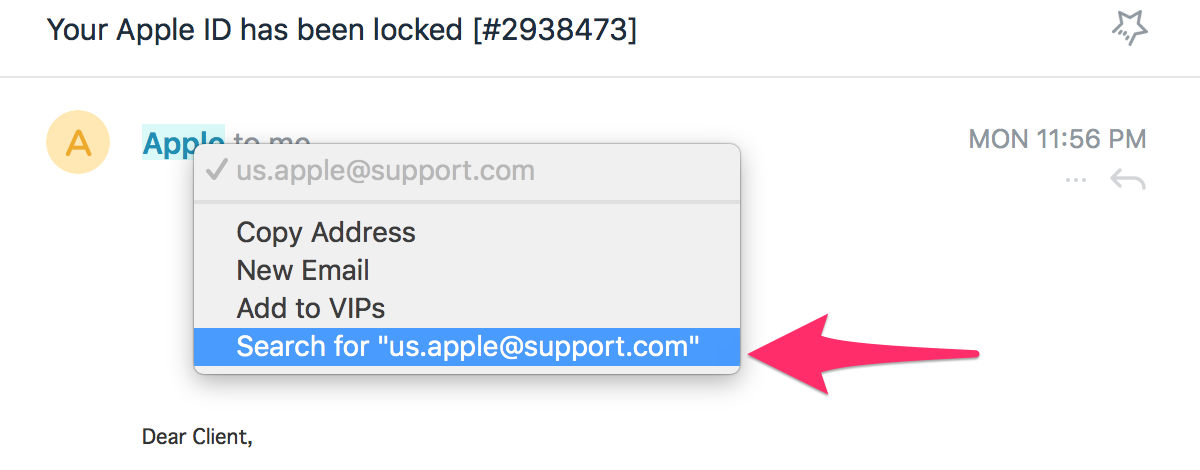
But, when I checked the email from which I got this message, I could see that it was not by Apple but from the domain support.com. This is the first sign that will tell you that you don’t believe in such a request you get.
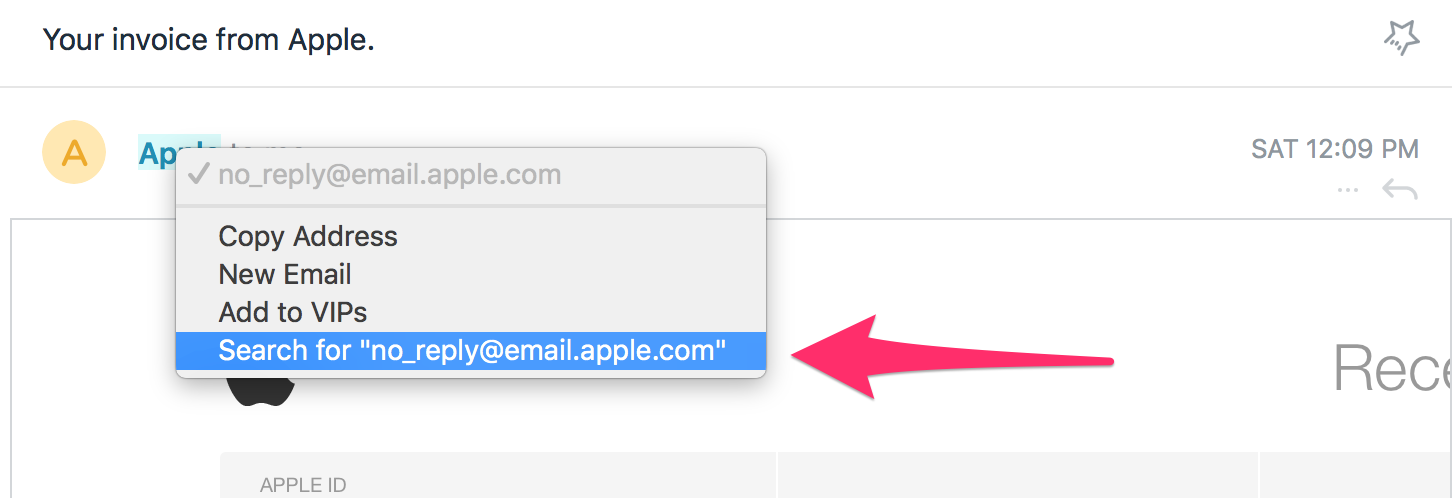
And here is the screen from the email message that I receive from Apple each month. As you can see, they use their own domain address to send emails. The same cases I have with Amazon and many other providers. They are interesting because of the possible credit card information.
Questions You Need to Ask Yourself Before You Make a Final Decision
Before you decide to send the required data, you will need to check these several things:
Who sent you an email? When you look at an email, first check the “from” field. You will see the sender’s information at the top of the message. There are two types of information that can be found in this area. The first is the name of the sender and the second is the sender’s email address.
Who has received such an email? Another part of the email that needs to be checked is the “To” field. If there are many other recipients, there is probably something wrong with this sender.
Is there anything as an attachment to the email message? When you receive an unknown email attachment, it may indicate that the message is not legitimate.
What is the subject of the email message? Fraudsters would especially like from you to open their messages, so they often use the title of the message to attract your attention. These subjects are some of the most used by phishing attackers:
- “Final reminder: Notice of Tax Return.”
- “Service cancellation in 10 days.”
- “Are you at your desk?”
- “Your account has been locked”
- “Notification of Personal Information Error”
- “Notice of payment.”
- “University Terror Alert”
- “Notice of appearance in court.”
- “YOUR ACCOUNT HAS BEEN SUSPENDED !!!”
- “Urgent”
- “Emergency Alert!”
- “Congratulations, you won!”
- “You won’t believe these photos.”
What does the email message say? Some phishing messages can be very persuasive. Others are less persuasive. First, if you receive an email where there is very little or no content other than a hyperlink, it’s almost always a scam of some sort. Do not click on the link!



