The design phase of a startup is the most challenging and important. It’s crucial to understand how to design a business model. Most businesses fail because they can’t create a proper model.
The most important thing about building a startup is understanding how to build a business model. To do this, you have to think about how your customers could use your product and how they will be affected by each option.
Before starting the development of a digital startup, it’s vital to define how it will make money. The way you generate profit through a new product is defined by its business model. Here you will learn the best product design practices for outlining a winning business model for a startup.
Business model canvas
A business model is a strategic plan on how your product will deliver value to users in exchange for their money. To set the right decisions, you need to deeply understand the customer needs, your business’s value proposition, and the suitable cost structure that will keep the product profitable over the long run.
A business model canvas designed by Alexander Osterwalder helps startups define all these aspects to get the desired business outcomes from the product.

The right part of the canvas describes the market and target customers. The left side focuses on the business’s internal factors, and the bottom part describes the values the product will deliver to users (value proposition).
How to map a business model using a canvas
Step 1: Outline your customer segments
Customers are at the heart of any business model. Without profitable customers, the company cannot survive in the long term.
A customer segment is a group of people with similar needs. You can reach them through the same channels, and you want to reach and serve specifically those customers. We can group them into different segments with common needs, behaviors, or other attributes for better customer satisfaction. You can define one or several different segments inside business models.
Think over the market type your future product is for. The major market types include:
- Mass market: No segmenting of the target audience. All customers have similar needs.
- Niche market: A product is for particular customer categories with distinct needs, values, etc.
- Segmented: A product is intended for two or more customer segments with different needs yet related problems.
- Diversified: A product is designed for two or more customer segments with distinct needs and concerns.
- Multi-sided markets: A product is aimed at interrelated customer segments.
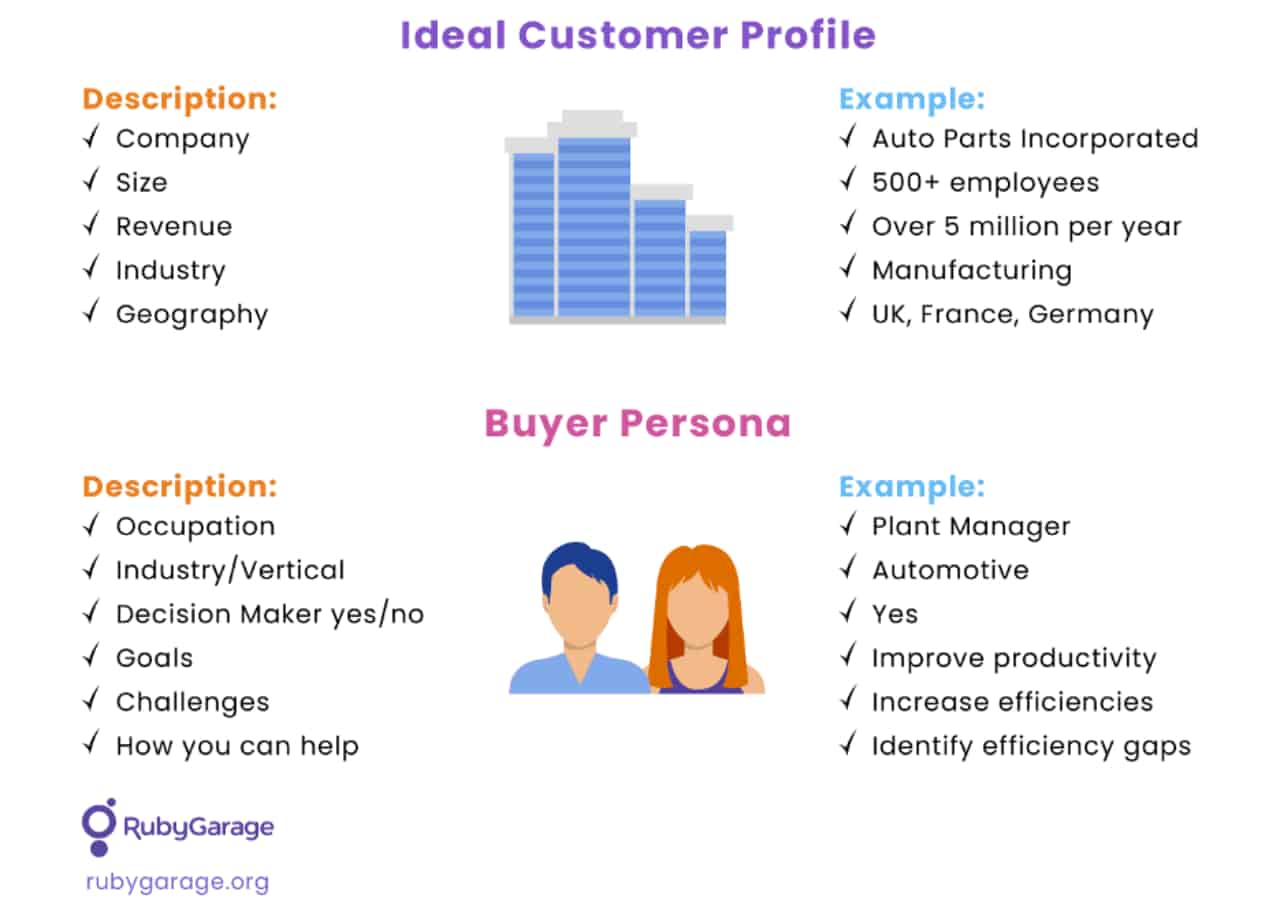
Then, define your user categories and describe their behavior, needs, problems, and demographic characteristics. Group these details into each segment’s ideal customer profile (ICP). It would be great to develop a buyer persona for each ICP:
Step 2: Set value proposition
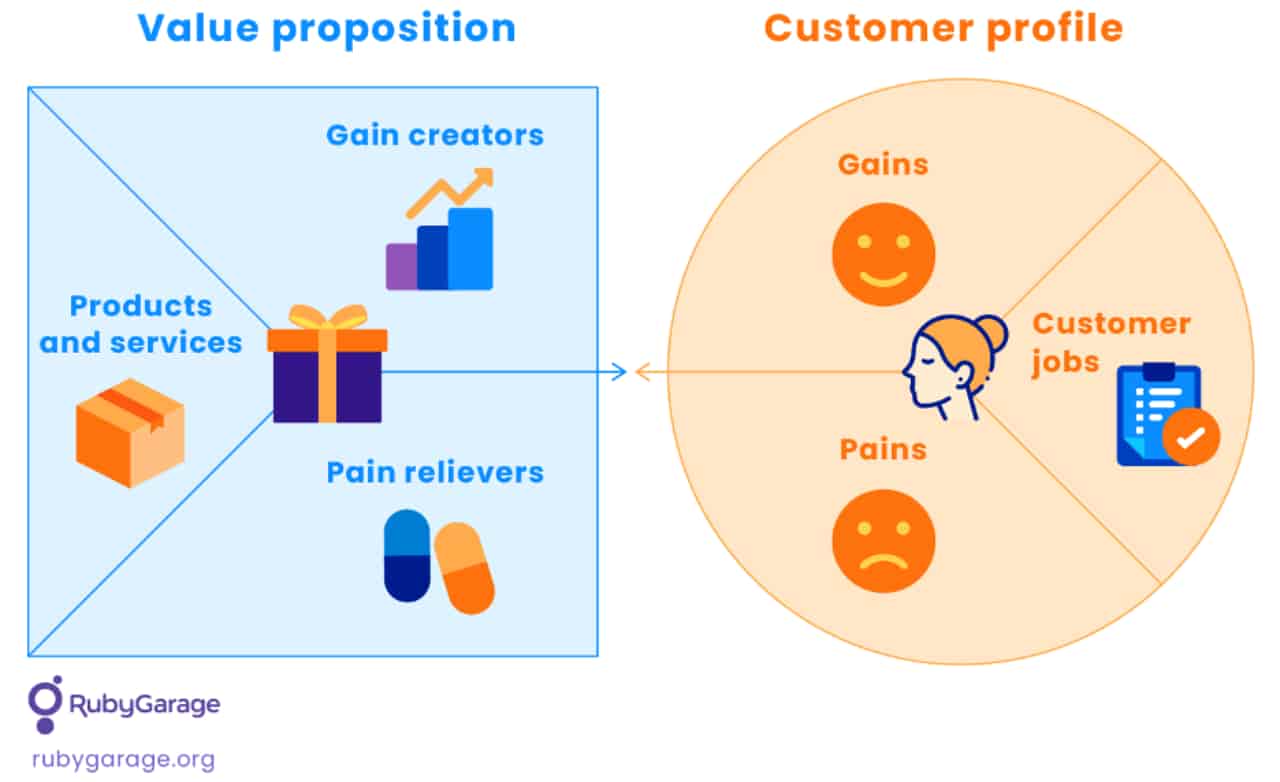
The value proposition is one of the most critical elements of the business model: it is the reason that customers choose one company over another. A list of features and benefits that can contribute to creating value for customers includes newness, performance, customization, design, brand, price, cost reduction, and risk reduction. It is why a customer may prefer your product over others.
Because these elements can significantly influence a customer’s buying decision, having the right mix of these elements will help ensure the company’s success in terms of revenue and profitability.
In a perfect scenario, it is a unique value a user cannot get with any alternative. It can be the benefits in performance, convenience, risk reduction, newness, price, status, etc. The value proposition should match your target customer profile to make the product deliver exactly what customers look for on the market.
✋ Warning
Follow this step-by-step guide to build your superior value proposition to become number one on the market and stay in that position.
Step 3: Channels
Channels inside the business model will explain how your company communicates with customers and will deliver value to defined customer segments. Communication, distribution, and sales channels are part of the channels and how your company will communicate and deliver value.
The value proposition is delivered to customers through specific channels. These are also how customers find the solution on the market and start the sales cycle.
The channels can be:
- Direct: a company website or in-house sales channels
- Indirect: stores owned by the company
- Partner: sites, stores, and other selling points owned by other companies.
Partner channels require less investment yet imply paying a commission for sales, and you potentially lose a part of your profit. Direct channels bring higher margins but are more resource-consuming for arranging, operating, and managing.
Step 4: Map customer relationships
Customer relationship, as a part of the business model, describes the relationships your company will establish with specific customer segments you have defined previously.
The goals of customer relationships can cover the following:
- How will you get new customers?
- How will you increase the customer retention rate of current customers?
- How you will increase income through some types of up-selling and cross-selling.
Customer relationships fall into several categories: transactional, long-term relationship, personal assistance, dedicated personal assistance, self-service, automated services, communities, co-creation, etc.
Set how you will build relations with customers based on your customer segments’ expectations, goals, and preferences. Also, consider the product’s nature and your business goals. Here are some most popular types of relationships:
- Personal assistance
- Dedicated personal assistance
- Self-service
- Automated services
- Communities
- Co-creation
- Transactional relationships
Often, companies offer a range of options to choose from.
Step 5: Define the revenue streams
This part of the business model describes how the company generates cash from each customer segment previously defined. According to Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur, revenue streams are the arteries if customers are the heart of a business model. You can generate different revenue streams from each of your customer segments.
A business model can involve two different revenue streams:
- Transaction revenues from one-time customer payments where customers come to the company to buy something and will never return or soon purchase again.
- Recurring revenues from ongoing payments for products and services that customers will pay in a specific time interval to use the product and service.
✋ Warning
Follow this guide to build your revenue model using the answers to six important questions.
You can generate revenue in many ways based on what your customer types are willing to pay for and how they prefer to do it. The typical revenue streams for digital products include:
- Usage fees
- Subscription fees
- Licensing
- Landing/leasing
- Asset sales
- Brokerage fees
- Advertising
Step 6: Set key resources
Resources are also crucial for the success of startup companies because they describe the most important resources that will ensure your business model works properly. Key resources for achieving success fall into four categories: physical, intellectual, human, and financial.
To run any business, you need specific resources. A business model cannot be realized without the necessary resources to create and deliver the value proposition, communicate with customers, earn revenue, and grow the company.
In product design, you need to plan resources to develop a product, launch and promote it on the market, maintain customer relationships, process orders, and generate revenue. Define and list all physical, intellectual, human, and financial resources to make your startup live.
Step 7: Define key activities in your business model
Key activities of the business model will explain the most important things your company will need to do to ensure that the business model is functional. A company’s operations or problem-solving activities are also essential to its success. Operations activities can include designing, manufacturing, and delivering. Problem-solving activities include knowledge management, continuous training, and maintaining platforms or networks.
Key activities describe the actions you need to run your business. These actions include
- Production: The product design, development, and delivery
- Problem-solving: The efforts to solve specific customer problems
- Platform/network: If you run as a platform, you’ll need steps to arrange its management, promotion, maintenance, etc.
Step 8: Identify key partnerships
The development of partnerships at the startup stage is an important success determinant for startup companies because this element of the business model will describe the network of partners that will be important for normal operations of the business model.
Most companies depend on strong partnership networks to achieve more and with higher efficiency than they could achieve alone.
If your business relies on suppliers and other partners, identify all these connections considering optimizing operations, reducing costs and risks, creating economies of scale, and providing all required supplies. List the following key partnerships:
- Non-competitor partnerships
- Collaboration with competitors
- Buyer-supplier relations
- Joint ventures.
✋ Warning
Here is a step-by-step guide for building an innovation network that will allow your organization to be more effective in the long run.
Step 9: Set the cost structure
The cost structure describes all costs required to operate a business model and is another element that will define the potential for success of the startup company, as it directly impacts the profitability of a company and its growth potential. It includes all fixed and variable costs that form the product price and expenses for its production, maintenance, and distribution.
The type of cost structure that the business model will require is an essential determinant in reaching success.
Your startup may have a value-driven or a cost-driven cost structure. The first one focuses on maximizing the product’s value even if it implies a higher product price. The second one focuses on minimizing product costs.
Key takeaways
As you can see, when you transform your idea into a business model canvas, you will have many elements in each building block on the business model canvas. When you fill out your business model canvas, you’ll obtain a helicopter view of all resources and processes and their interconnections required to produce and operate your business. The canvas blocks are interdependent.
For instance, each value proposition is related to a specific revenue stream and customer segment. You can choose a suitable business model based on the filled-in canvas and validate your assumptions by running proper tests. The validated business model is a proven basis for mapping out the product development strategy and roadmap. Apply for a reliable product design services provider to implement your startup product effectively according to your strategy and business goals.



