Freelancing offers flexibility and independence, but it also comes with the responsibility of managing your finances and taxes effectively.
In this article, we’ll dive into the world of invoicing for freelancers, providing essential tips to streamline your financial processes, offering insights into tax considerations, and sharing financial strategies to ensure your freelance journey is a financially successful one.
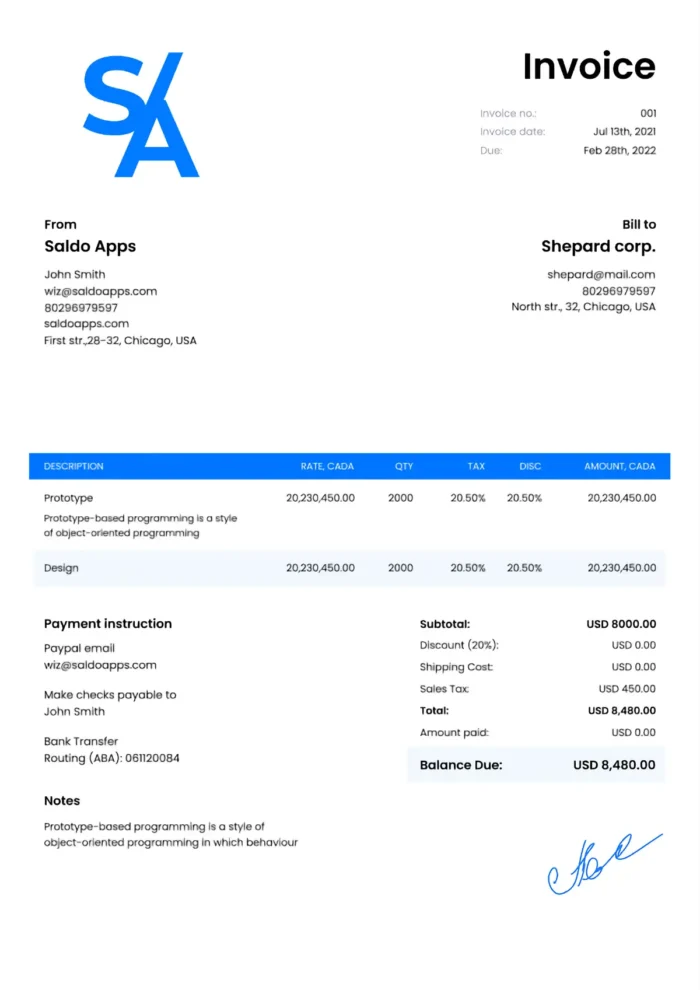
Essential Invoicing Tips for Freelancers
Efficient invoicing is the cornerstone of freelance financial management. Here are some crucial tips for freelancers to streamline their invoicing process:
- Professional Invoices: Create a professional-looking invoice. Create an invoice that includes your contact details, a unique invoice number, payment terms, and a breakdown of services rendered.
- Clear Payment Terms: Clearly specify payment terms on your invoices, including due dates and accepted payment methods. This helps avoid payment delays.
- Detailed Descriptions: Provide detailed descriptions of the services you’ve rendered. This clarity helps clients understand the value you’ve delivered.
- Invoice Promptly: Send invoices promptly after completing a project or reaching a milestone. Timely invoicing improves your chances of receiving prompt payments.
- Use Invoicing Software: Consider using invoicing software to automate invoice generation, track payments, and send reminders. This saves time and reduces administrative overhead.
- Set Aside Taxes: Dedicate a portion of your earnings to cover taxes. Freelancers are responsible for their tax payments, so it’s essential to save accordingly.
- Track Expenses: Keep meticulous records of your business expenses. Many expenses can be tax-deductible, reducing your overall tax liability.
- Invoice in Advance: To ensure a steady cash flow, consider invoicing for a portion of the total fee upfront for long-term projects.
Tax Considerations for Freelancers
Freelancers often have unique tax considerations compared to traditional employees. Here are some important tax considerations for freelancers:
- Self-Employment Taxes: Freelancers are considered self-employed, which means they are responsible for paying self-employment taxes, including Social Security and Medicare taxes. Be prepared for these additional tax liabilities.
- Quarterly Estimated Taxes: Freelancers may need to make quarterly estimated tax payments to cover income and self-employment taxes. Failure to do so may result in penalties.
- Tax Deductions: Familiarize yourself with tax deductions available to freelancers. Common deductions include home office expenses, business-related travel, and professional development costs.
- Tax Credits: Explore tax credits that may apply to your freelance business, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit or the Child and Dependent Care Credit.
- Tax Professionals: Consider working with a tax professional who specializes in self-employment tax issues. They can help you navigate complex tax regulations and maximize deductions.
Financial Strategies for Freelancers
Freelancers often have irregular income, making financial planning essential. Here are some financial strategies to help freelancers manage their finances effectively:
- Budgeting: Create a budget that accounts for both business and personal expenses. This helps you manage your cash flow and plan for expenses.
- Emergency Fund: Build an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses or income fluctuations. Aim to have three to six months’ worth of living expenses saved.
- Retirement Planning: Freelancers do not have employer-sponsored retirement plans, so it’s crucial to set up and contribute to your own retirement accounts, such as a SEP IRA or a Solo 401(k).
- Invoice Tracking: Keep track of invoices, payments, and outstanding balances. This ensures you stay on top of your cash flow and can follow up on overdue payments.
- Client Contracts: Use clear and comprehensive contracts outlining project scope, payment terms, and deadlines. Contracts help protect both you and your clients.
- Income Diversification: Consider diversifying your income streams by offering additional services or products related to your freelance expertise.
- Regular Financial Check-Ins: Schedule regular financial check-ins to assess your income, expenses, and progress toward financial goals.
Conclusion: Freelance Financial Success
Freelancing can be a rewarding career path, but it comes with financial responsibilities. Effective invoicing, understanding tax considerations, and implementing sound financial strategies are essential for freelance success. By following these tips and staying proactive in managing your finances, you can thrive as a freelancer while securing your financial future.





