Do you have all the required key managerial skills to manage your company? Can you be a good manager with all the essential management skills necessary for you and your company?
Business owners are entrepreneurs until they become managers. When they become managers, they will feel frustrated because they need to deal with new problems – managerial problems.
Formalization inside your company requires more managerial skills, training, and development. Such an expansion will require different management skills and capabilities across the company. So, this is the right time to change yourself and your company’s operations.
Why Will You Need Managerial Skills?
Being a good manager is difficult because you will need some managerial competencies. People with the right competencies and key management skills will move from the bottom to the top levels.
I remember when I got my first managerial position; it was exactly 20 years ago when I became deputy chief at the office. That place required four years of experience, and I was assigned with only two years. Why? First, I have already learned and implemented all procedures in the customs office. Second, I have built good relationships with all my colleagues, and because of my showcase of doing everyday technical tasks, they believe me, and in such a way, I have already built my leadership skills. Third, I know a little bit about management roles because of my academic work on a master’s degree and then on a Ph.D.
Then, after two years in that position, I got a new job where I managed other people in the intelligence department again. The principles were the same: I showed strong knowledge and technical abilities through previous practical experience, so they started looking at me as a leader.
Both of these cases were related at the first-line managerial level. But, when I get a middle management role, the same things was important for success. This was really important because I was much younger and without years of work in an organization like my team members, so at the beginning, they didn’t believe me. Also, I have people with different competencies and need time to find a way how to utilize them in the right way so the department will achieve the best possible outcomes from each of them. So, in this case, I needed to look at the department as a whole.
When I started my own company in 2007, I practiced top management and started to work as a consultant for small, medium, and several large companies. I’ve seen many good things but also many bad things when it comes to the principles of managing people.
What I can say that is common for each of my own and as a consultant experience is that good managers can transform poor teams into great ones, and bad managers can make great teams perform poorly.
So, you need strong management skills because you cannot succeed if your team performs poorly.
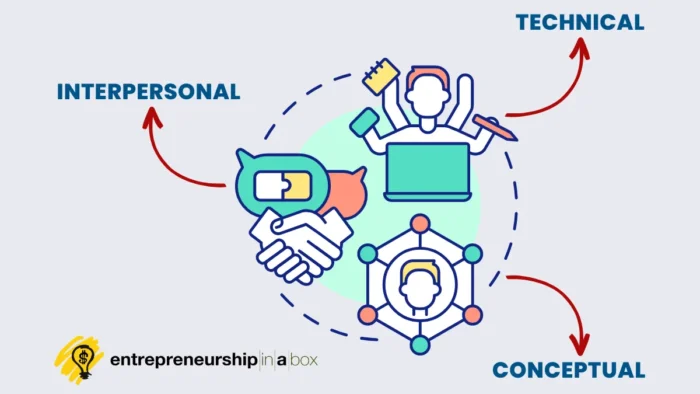
What Are Management Skills?
Management skills definition: the knowledge and ability of the individuals in a managerial position to fulfill specific management activities or tasks.
As with any skill, you can learn and practice your key management skills and be ready to become a successful manager.
Many theoretical definitions include discussion about talent.
Talent is personally related to an individual and shows a natural gift from nature about something inside that talented person.
When we talk about managerial skills, we talk about the abilities of a manager to maintain high efficiency in how his or her employees complete their everyday tasks. Because of that, managers will need skills that will help them manage people and technology to ensure an effective and efficient realization of their working duties.
3 Types of Management Skills
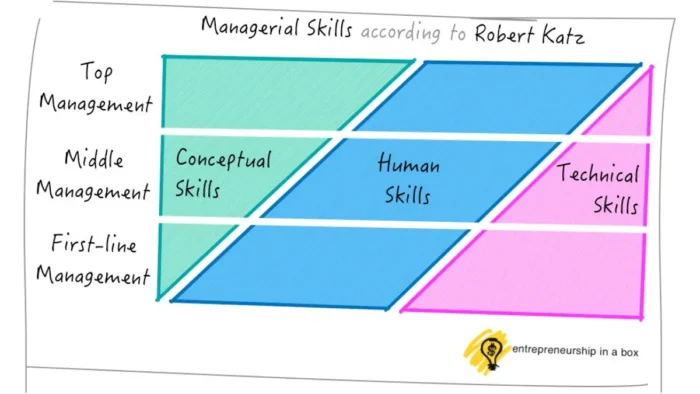
An HBR article, Skills of an Effective Administrator, by Robert Katz, highlights three key management skills: technical, conceptual, and human or interpersonal skills as the most common management skills.
1. Technical Skills
Technical skills are related to the mechanics or step-by-step actions of doing things. Or, what will you need to do as a manager, and how do you do it?
So, these are the skills needed to do certain “jobs” within the company.
These skills are most important for first-level managers. When it comes to the top managers, they are not something with a high significance level. Technical skills lose their importance as we go through a hierarchy from the bottom to higher levels.
2. Conceptual Skills

Conceptual skills are the managerial ability to engage in more abstract thinking.
You can see the big picture by analyzing various things. In such a way, you can predict the future of the business or department as a whole.
So, good managers understand the complexity of the entire organization and see the organization as a whole.
Often, what is in the interest of the whole is not necessarily in the interest of some functions or parts of the business. And here comes the “job” of a manager, which is to make the best-informed decisions for the organization as a whole.
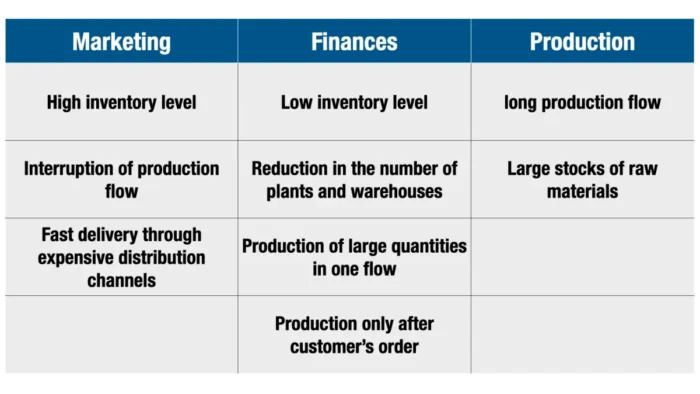
First, each company has several business elements, such as sales, marketing, finance, production, etc. All of them have different goals, even completely opposing ones. For example, marketing wants to keep a higher stock of products on hand to ensure a rapid response to customer demands. But, reducing stocks is essential for reducing expenses for the financial department. Contrarily, a continuous manufacturing flow requires a higher supply of raw materials in inventory.
Also, because marketing must keep up with customers’ ever-evolving expectations, the production flow must be море frequently interrupted.
On the other side, finance and manufacturing will require longer production flows in large quantities and in one flow. They want to maintain a stable production system at lower costs.
Related: Real-life Organizational Decision-Making Examples
With these skills, you look outside your department’s goals and make decisions that satisfy overall business goals. Also, they are essential for top managers and less important for middle and first-level managers.
As you move up in the managerial hierarchy, from the bottom to the top, the importance of these competencies will rise.
3. Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal management skills, also called human skills, are related to a manager’s ability to influence others to get things done. When you are a manager, interacting with other people is essential.
Without employees, there is no need for management skills.
To succeed as a manager, you need to have the ability to lead teams more effectively. Motivate your subordinates to achieve excellence and help them use human potential more effectively in the company.
Strong interpersonal skills are essential for managers on all hierarchical levels in the company.
Related: The Team Effectiveness and Different Roles in Teams That Win
Examples of Management Skills in Each Category

Now, let’s look at some examples of each of the above-mentioned most important management skills.
Related: Unlocking the Secrets of Effective Management Style
Technical
When it comes to these skills, as I already discussed previously, they are about the mechanics or ability to do a specific job or task. For example, you have these skills if you are proficient in graphic design.
For example, let’s take an individual who works in the sales department and has highly developed sales competencies achieved through education and experience in his department or the same departments in different organizations. Because of that, this person can be a perfect solution to become a sales manager. This is the best solution because he has excellent skills related to the sales department.
On the other hand, the person who becomes a sales manager will start to build his next type of required skills, like conceptual and interpersonal. It is because if his task until now was only to work with the customers as a sales representative, now he will need to work with employees in the sales department in addition to working with customers.

Conceptual
Here are some examples of conceptual management skills that good managers will need to have:
- Strategic thinking. An essential part here is strategic thinking to see things that others don’t see. You need to plan ahead and improve your tactics based on what you have experienced and learned.
- Planning skills. Because you can see all aspects of your business, you must translate this potential with strategic planning skills. You want your vision to become true through achieving strategic goals and implementing action steps from your plan.
- Being analytical. You need to be analytical to make the right decisions. This is the ability to see something in numbers, relate different information, and conclude.
- Being entrepreneurial. These competencies can also help you make your vision a reality. Abstract ideas, connecting the dots, and changing the world are only a few of the abilities that they will bring you.
Related: 10 Reasons Being An Entrepreneur Is Better Than Employment
Human/Interpersonal
Let’s look at some examples here:
- Leadership skills are important for creating enthusiasm among employees to create new and better ways of doing their jobs. As a manager, you need leadership skills to inspire and motivate. Your leadership style must ensure that all team members will put their full efforts into achieving the business’s strategic goals.
- Emotional intelligence is the ability to empathize and understand people around you, even when they disagree with you.
- Delegation skills will be important for your success. Delegating tasks means dividing the workload among your team members and delegating tasks according to their ability. It is important that you understand who can do what task and how much time each person will need for a certain job.
- You can not underestimate listening skills or actively listening to your team members, customers, partners, and other stakeholders.
- Conflict resolution skills, or resolving conflicts, are crucial management skills. Healthy conflicts for an organization are those that result in better decisions and methods of doing things. But, after some point, the conflict can become counterproductive for the company’s performance (see the image below).
Related: Uncovering the Psychologists’ Theories of Motivation: What Drives Human Behavior?

- Communication skills are essential if you want to have an effective communication process. You must communicate effectively with customers, employees, partners, investors, stakeholders, etc. So, communication skills are important for you. You cannot manage without direct communication with your team members and key management.
Also, you will need negotiation skills. To succeed as a manager, you must be a good negotiator prepared for a fair compromise.
But, There is One More Thing – Self-Management Skills
Thus far, we’ve discussed management skills related to different managerial positions.
However, what about self-management?
You want to accomplish more of your professional and personal goals each day. So, you will also need skills to manage yourself.
Related: 10 Smart Skills You Will Need Now as an Entrepreneur
Self-management skills are essential skills not only for managers but for everyone. These skills will help you to lead yourself in your everyday management tasks. Great managers and leaders know how to manage their time and their energy effectively. One of the most important self-management skills are time management and adaptability.
- Time management skills. The ability to manage your own time effectively involves setting goals and organizing and prioritizing tasks. Your productivity will become the mirror of your organization’s productivity. According to Mintzberg, managers:
“appreciated the opportunity cost of their own time, and they were continually aware of their ever-present obligations—mail to be answered, callers to attend to, and so on. It seems that a manager is always plagued by the possibilities of what might be done and what must be done.”
– Mintzberg
Related: Find Your Rhythm: How Inspirational Music Increases Productivity at Work
- Adaptability. Today, change occurs quickly, so the skills and expertise you have right now will be outdated tomorrow. You must have the characteristics of adaptability as a key management skill and be ready for the future.
Related: 9 Self-Management Skills and How to Improve Them
Are There More Management Skills?
Some authors highlight the significance of other skills, such as controlling and decision-making skills. But I realize they’re just part of one of the above-mentioned categories.
Let’s take the example of controlling skills.
Controlling can’t be a skill but rather a process or one of the managerial functions. Usually, many managers control their employees through interpersonal skills and analytical skills (tracking their performance), which we have already described previously.
I have also found that problem-solving and decision-making skills are other managerial skills.
Decision-making is also a process (part of the problem-solving process) rather than a skill. Better judgment will result from developing your own conceptual skills. If we talk about specific technical problems, then problem-solving skills will be part of technical skills.
✋ Warning
Learn more about decision-making as a part of the problem-solving process, decision-making models, and two techniques to make better decisions in the introduction to the decision-making process.
All effective managers will need technical, conceptual, interpersonal, and self-management skills. If you want to work on developing management skills, read our article about management training programs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Management skills are the knowledge and ability of the individuals in a managerial position to fulfill specific management activities or tasks.
Three management skills identified by Robert Katz are technical, conceptual, and interpersonal, also called “human.”
Managers are responsible for running the organization effectively and ensuring everyone works together toward a common goal. Without managerial skills, effective managers cannot manage employees to achieve the organization’s goals.