Collaboration is the key to successful teamwork that unlocks a world of possibilities. When individuals come together, pooling their skills, knowledge, and resources, they can achieve goals that seem impossible on their own. However, the power of collaboration extends beyond simply working together. It involves a delicate balance of different roles, each with its own unique contribution to the team’s success.
At the heart of successful collaboration are team members who are willing to listen, communicate, and share ideas. These individuals bring their expertise to the table, enhancing the team’s collective knowledge. Some leaders guide the team’s direction, motivators inspire and encourage, problem solvers find creative solutions, and coordinators ensure that tasks are completed efficiently. Each role is essential and interdependent, forming a cohesive whole that is greater than the sum of its parts.
In this article, we will explain the different team effectiveness models and roles in successful teamwork, exploring how they contribute to the team’s overall effectiveness. Whether you’re a manager, a member, or someone interested in enhancing collaboration and team skills, understanding these roles is crucial for achieving success in any collaborative endeavor.
The Foundation of Team Effectiveness
Team effectiveness can make or break an organization. Effective teamwork is the cornerstone of any successful organization. Understanding different team effectiveness models can provide valuable insights into how to create, manage, and optimize high-performing teams.
Using one of these team effectiveness models can help you identify your employees’ strengths and address their challenges to maximize performance and results. Knowing more about the various models that can promote greater efficiency among teams may help you determine which one of many team effectiveness models is right for you.
Here, we will mention six popular team effectiveness models: Hackman’s Five Factor Model, The Katzenbach and Smith Team Effectiveness Model, the Input-Process-Output (IPO) Model, Lencioni’s Model, the GRPI Model, and the T7 Model.
1. Hackman’s Five Factor Model
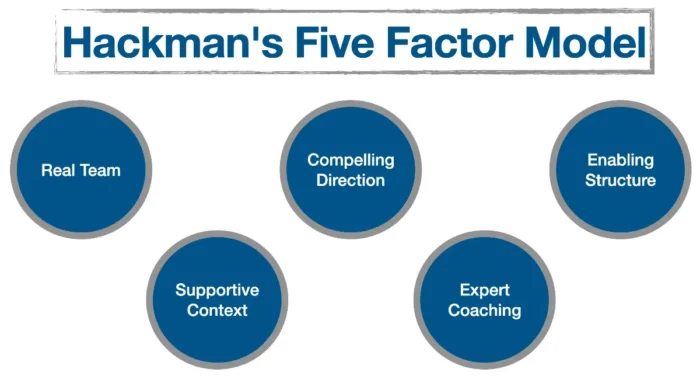
This team effectiveness model suggests that team effectiveness is determined by the team’s ability to stay together (team viability), the quality of their output (task performance), and the personal growth of members (individual learning).
Hackman’s team effectiveness model identifies five factors that lead to team effectiveness:
Real Team
A “real team” is more than just a group of individuals working together. It’s a cohesive unit with clear boundaries, interdependencies, stability, and authority over its work that ensures appropriate team performance. Members of such a team understand their roles and how their contributions and team relationships fit into the larger picture.
For example, a surgical team in a hospital is such a team where each member, from the lead surgeon to the anesthesiologist, has a specific role and relies on each other to complete a surgery successfully.
Compelling Direction
A “compelling direction” serves as a roadmap for an effective team. It’s a clear, engaging, and challenging goal that guides the team’s decisions and actions.
For example, NASA’s “Moon Shot” project in the 1960s provided a compelling direction that motivated and guided thousands of scientists, engineers, and astronauts toward the common goal of landing a man on the moon.
Enabling Structure
An “enabling structure” refers to the organization and processes within an effective team. This includes well-defined roles, clear communication channels, and mechanisms for feedback and conflict resolution.
For example, a successful software development team might have an enabling structure that includes roles like project manager, lead developer, and quality assurance specialist, along with processes for daily stand-up meetings and code reviews.
Supportive Context
A “supportive context” ensures that individual team members have the necessary resources, information, and support they need to do their jobs effectively and ensure a high level of team performance. This includes both tangible resources like tools and software and intangible ones like a positive organizational culture and supportive leadership.
For example, tech companies like Google create a supportive context by providing employees with state-of-the-art tools, flexible work policies, and a culture encouraging innovation.
Expert Coaching
The last factor, “expert coaching,” provides teams with guidance and feedback to help them improve the team’s success and overcome all possible challenges. A good coach can help members develop new skills, navigate interpersonal issues, and focus on their goals.
For example, a sales team might benefit from a coach who can provide feedback on their sales pitches, help them understand customer needs, and motivate them during challenging times.
Related: Unlocking the Secrets of Effective Management Style
2. The Katzenbach and Smith Model
The Katzenbach and Smith team effectiveness model is a highly respected framework in the field of organizational development. It was developed by Jon Katzenbach and Douglas Smith, renowned experts in team dynamics, based on their extensive research and experience.
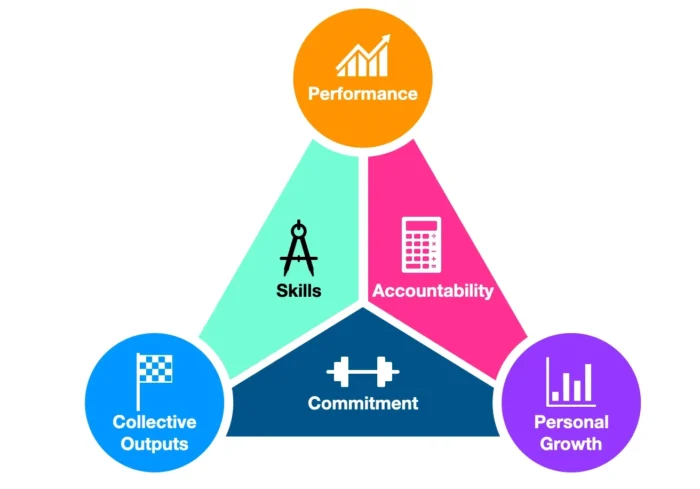
The Katzenbach and Smith model has three main aims represented by the triangle’s points. These aims are:
- Personal growth focuses on monitoring each team member’s progress to maintain their motivation, productivity, and satisfaction with their professional development.
- Collective output refers to the deliverables from the team, which are a crucial objective and a quantifiable sign of success.
- Performance results aim to ensure that the team’s work process is effective by eliminating waste and improving productivity and efficiency.
According to Katzenbach and Smith, the effectiveness of a team is not merely determined by the skills of its members but rather by three critical factors:
- Shared Commitment: understanding and agreement among team members about the team’s goals and objectives. When a team has a shared commitment, each member is motivated and invested in achieving these goals.
- Complementary Skills: effective teams comprise individuals with diverse yet complementary skills. These skills can be technical (such as coding or project management) or soft skills (like communication or problem-solving). The idea is that each team member brings something unique to the table, contributing to a whole that is greater than the sum of its parts. A successful marketing team, for example, might include members skilled in graphic design, content writing, data analysis, and social media management.
- Mutual Accountability: The third factor is mutual accountability, which means that each team member takes responsibility for their tasks and feels accountable to the rest of the team. This promotes a sense of ownership and encourages everyone to perform at their best. For example, in a customer service team, each member might be accountable for resolving a certain number of customer queries each day.
3. Input-Process-Output (IPO) Team Effectiveness Model
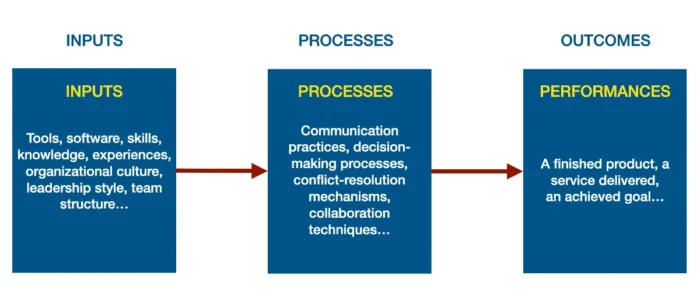
The IPO model is a framework for understanding team dynamics and improving the performance of the team. It was developed to offer a clear and structured way to view how different aspects of teamwork interact and impact outcomes.
Input
The Inputs are the resources a team has at its disposal as it begins to work on its tasks. These can include tangible assets like tools or software but also intangible elements such as skills, knowledge, and members’ experiences. Organizational culture, leadership style, and team structure are other examples of inputs.
Consider a marketing team tasked with launching a new product. The inputs might include their budget, the members’ expertise in marketing strategy, and the company’s established brand identity.
Process
The Process component refers to how the team utilizes these inputs to accomplish their tasks. This includes communication practices, decision-making processes, conflict-resolution mechanisms, and collaboration techniques. The process aspect is crucial because it determines how effectively the inputs are translated into outputs.
Related: Real-life Organizational Decision-Making Examples
In our marketing team example, the process might involve regular brainstorming sessions, a clear division of responsibilities, and periodic progress reviews.
Output
Finally, Output represents the results produced by the team. This could be a finished product, a service delivered, or an achieved goal. Outputs are typically what the team and the organization measure to calculate the effectiveness of the team.
For the marketing team, the output could be the successful launch of the new product, measured by indicators like sales figures, customer feedback, and increased brand recognition.
So, the IPO model suggests that effective teams are those that can efficiently transform inputs into outputs through well-managed processes. As such, it provides a valuable lens for identifying team performance issues and determining where improvements can be made. For example, suppose a team is not producing the desired outputs. In that case, team leaders might examine whether the issue lies in the inputs (such as insufficient resources or skills), the process (like poor communication), or a combination of both.
4. Lencioni’s Team Effectiveness Model
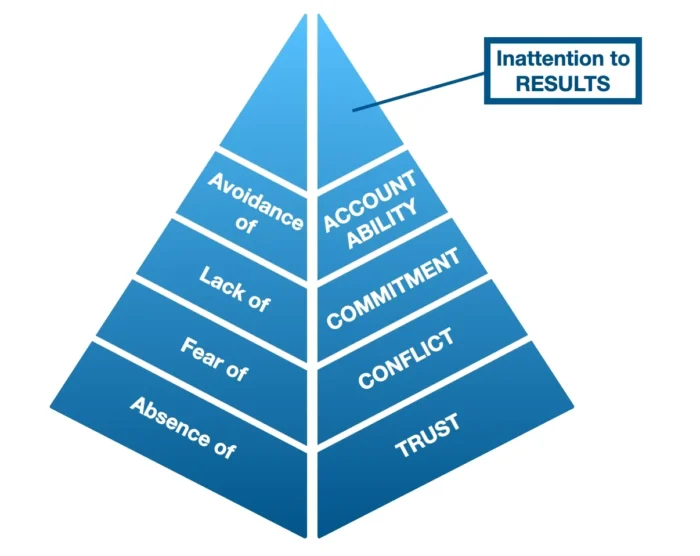
A renowned management consultant Patrick Lencioni proposed a unique model to understand and enhance team effectiveness. This model, often called “The Five Dysfunctions of a Team,” seeks to identify common traps that teams might face and provides strategies to overcome them.
1. Absence of Trust
The foundation of Lencioni’s model is trust, which he defines as the confidence among members that their peers’ intentions are good and there is no reason to be protective or careful around them. In other words, the members are comfortable being vulnerable with each other about their weaknesses, mistakes, fears, and behaviors.
2. Fear of Conflict
The second level addresses teams’ natural tendency to avoid conflict. According to Lencioni, teams that trust each other are not afraid to engage in passionate dialogue and debate. This doesn’t mean personal attacks but rather a willingness to disagree over key issues in search of the best possible solution.
3. Lack of Commitment
The third dysfunction is a lack of commitment, which arises from the absence of clear or active agreement on decisions. Teams that engage in open discussion and then commit to a clear plan of action, even if it’s not everyone’s first choice, are more likely to succeed.
4. Avoidance of Accountability
The fourth dysfunction is the need for members to hold one another accountable to high standards. When teams don’t commit to a clear plan of action, even the most focused individuals hesitate to call their peers on actions and behaviors that may seem counterproductive to the team’s overall good.
5. Inattention to Results
The final dysfunction is inattention to results, where the members of the team put their individual needs or departmental considerations above the collective goals of the team. Effective team is results-oriented, measuring their success not by effort but by achievements.
Lencioni argues that teams can become more cohesive and effective by understanding and addressing these five dysfunctions. His model provides a useful framework for identifying issues within a team and developing strategies to overcome them, ultimately leading to improved performance.
5. GRPI Model
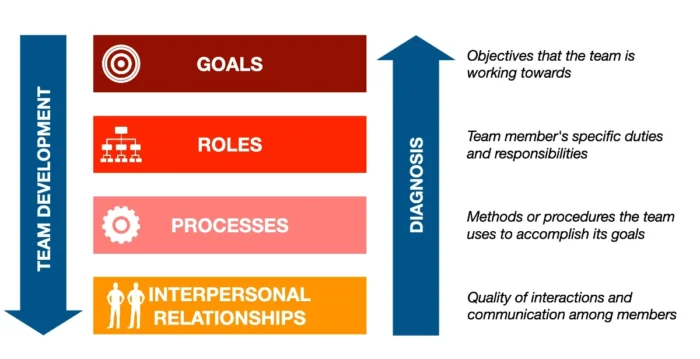
The GRPI team effectiveness model is a well-established framework for understanding and improving team effectiveness. Richard Beckhard developed it in the 1970s, and it has since become a staple in many organizations’ toolkits for team development. The model breaks down into four key components: Goals, Roles, Processes, and Interpersonal Relationships.
1. Goals
The first component, goals, refers to the shared objectives that the team is working towards. These should be clear, realistic, and agreed upon by all members. For example, a customer service team might aim to reduce response times to customer queries by 20% within the next quarter. Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals can help ensure everyone is on the same page and working towards the same end.
2. Roles
The second component, roles, is related to each team member’s specific duties and responsibilities. Clearly defined roles help prevent confusion, overlap, or gaps in work, ensuring everyone knows what they’re supposed to do and why it matters. For example, in a marketing team, one person might be responsible for social media management, another for content creation, and a third for analytics and reporting.
3. Processes
Processes are the methods or procedures the team uses to accomplish its goals. This includes how decisions are made, how communication is handled, how tasks are assigned, and how progress is tracked. Efficient processes can significantly improve a team’s productivity and effectiveness.
4. Interpersonal Relationships
Finally, interpersonal relationships refer to the quality of interactions and communication among members. This includes trust, respect, openness, and conflict management. Healthy relationships inside the members of a team can promote a positive team culture and improve collaboration between the members.
6. T7 Team Effectiveness Model
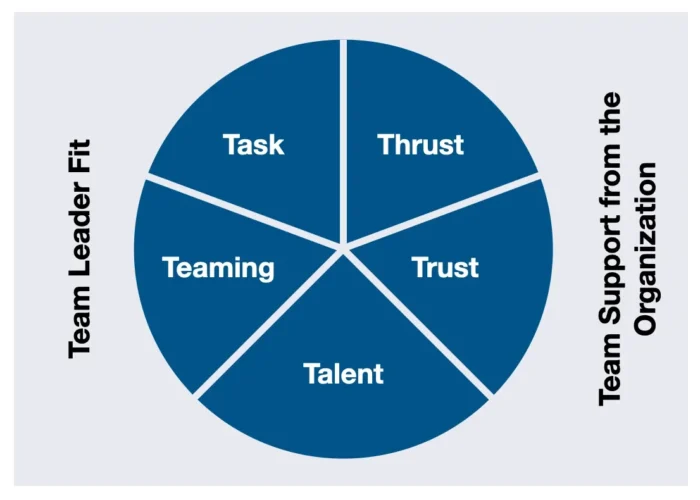
Dr. Michael Lombardo and Robert Eichinger developed the T7 Model as a complete framework that identifies seven factors crucial to team effectiveness. The model is divided into two categories: internal factors and external factors.
Internal Factors:
When it comes to internal dynamics, the model recognizes five internal factors:
- Thrust: This refers to the team’s shared understanding of their purpose and goals. To be effective, teams need clear, specific, and measurable objectives that all members are committed to achieving. For instance, a sales team might have a thrust to increase revenue by 15% in the next quarter.
- Trust: Effective teams are built on a foundation of trust. Members need to feel confident in each other’s abilities and intentions, comfortable with vulnerability and assured that their colleagues will perform their roles reliably.
- Talent: This factor relates to the members’ skills, knowledge, and capabilities. An effective team has the right mix of talent to accomplish its goals.
- Teaming Skills: These are the abilities necessary for working together effectively, such as communication, conflict resolution, collaboration, and decision-making skills.
- Task Skills: Task skills refer to the team’s technical competencies related to their specific tasks.
External Factors
There are also two external factors for high-performing teams:
- Team Leader Fit: This factor considers whether the team leader’s style and skills suit the team and its objectives well.
- Team Support from the Organization: Finally, teams need adequate resources and support from their organization to be effective. This could include budget, technology, training, or simply recognition and encouragement.
By focusing on these four internal factors and three external factors, teams can work towards improving their effectiveness. Remember, team effectiveness is not a static state but a dynamic process that requires ongoing effort and adaptation. The T7 Model provides a valuable roadmap for this journey, helping teams identify areas of strength and opportunities for improvement.
Understanding different team effectiveness models is vital for team development because there will always be some challenges that must be solved. Taking different elements from different team effectiveness models and implementing them in a specific situation will be important for the right team design and team management at different stages of the team’s lifecycle.
So, study different types of team effectiveness models and select the right team effectiveness model for you or a combination of some of them.
The Different Roles in Successful Teamwork
The most successful projects are often the result of a diverse team, each member bringing their unique skill sets, strengths, and responsibilities to the table. Here, we will get into the various critical roles for successful teamwork, emphasizing how each contributes to the team’s effectiveness.
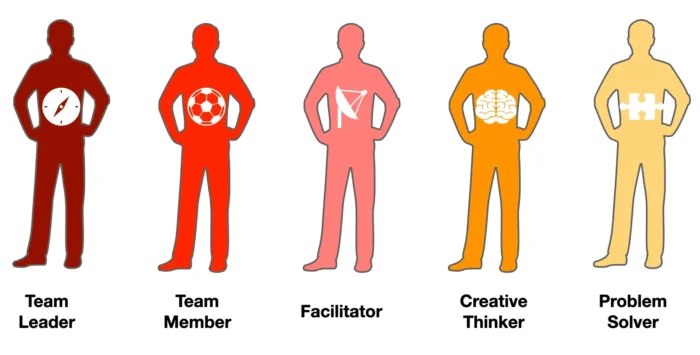
Team Leader: Responsibilities and skills
Effective team leadership is a critical factor in ensuring team success. It is crucial to have a leader who can guide and motivate the team to work together towards a common goal.
The leader inside a team is responsible for team leadership or guiding the team’s direction and ensuring everyone works towards the same goal. This involves setting goals, delegating tasks, and monitoring progress. A good team leader should have strong communication skills, be able to motivate the members, and be able to make difficult decisions when necessary.
In addition, a leader should be able to lead by example. It also means recognizing when they are wrong and being open to member feedback.
Team Members: Roles and Contributions
The members of the team are responsible for contributing their skills, knowledge, and resources to the team. This involves completing tasks assigned to them by the team leader but also being proactive and taking initiative when necessary.
In addition, team members should be able to work well with others. This means communicating effectively, listening actively, and being open to feedback. It also means working collaboratively to recognize other team member’s strengths and weaknesses.
Facilitator: Promoting Effective Communication and Conflict Resolution
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful collaboration. Without clear and open lines of communication, misunderstandings and conflicts can arise, hindering the team’s progress.
The facilitator plays a vital role in promoting effective communication within the team. This individual ensures that everyone can be heard and encourages active participation from all team members. They create a safe and inclusive environment where ideas can be freely shared without fear of judgment or criticism.
In addition to facilitating communication, the facilitator helps resolve conflicts during the collaboration process. Conflicts are inevitable when working with diverse individuals with different perspectives and ways of working. The facilitator acts as a mediator, helping the team members find common ground and reach a mutually beneficial resolution.
A good facilitator should have strong communication skills, remain neutral in conflicts, and help team members find common ground. They should also be able to recognize when conflicts are arising and take steps to address them before they escalate.
The Creative Thinker: Generating innovative ideas and solutions
Innovation is the lifeblood of successful teamwork. It is the driving force behind breakthrough ideas and solutions that can take a team’s work to the next level.
The creative thinker is someone who is not afraid to think outside the box and challenge the status quo. They bring fresh perspectives and ideas to the table, sparking creativity and innovation within the team. This individual encourages others to think creatively and pushes the boundaries of what is possible.
An excellent creative thinker should be able to approach problems from different angles, be open to new ideas, and be willing to take risks. They should also be able to communicate their ideas effectively and be able to work collaboratively with other team members.
To be an effective creative thinker, you must be open-minded and willing to explore new possibilities. You must be curious and eager to learn, constantly seeking inspiration from different sources. By adopting creativity, the team can tap into their collective imagination and discover innovative solutions to complex problems.
The creative thinker also plays a crucial role in fostering a culture of innovation within the team. They encourage risk-taking and experimentation, creating an environment where failure is seen as a stepping stone towards success.
The Problem Solver: Analyzing challenges and finding solutions
Challenges and problems are an unavoidable part of any collaborative work. Whether it’s a technical issue, a lack of resources, or a complex problem that needs solving, successful teams often face many roadblocks.
One of the critical roles in successful teamwork is that of the problem solver. The problem solver is responsible for analyzing challenges and finding solutions. This involves identifying potential roadblocks and developing solutions to overcome them.
A good problem solver should be able to think critically, be able to identify patterns and trends and be able to work collaboratively with other team members. They should also be able to communicate their ideas effectively and be willing to modify their approach based on feedback from other team members.
They are proficient at breaking down complex issues into manageable tasks and working collaboratively with the team to develop effective strategies.
A good problem solver understands the importance of active listening and open communication. They seek input from team members, valuing diverse perspectives and encouraging everyone to contribute their ideas. By fostering an environment of collaboration and open dialogue, the problem solver ensures that the team is collectively engaged in finding solutions.
To be an effective problem solver, you must have a strong analytical mindset and attention to detail. You must be able to think critically and objectively assess the situation at hand.
Ultimately, the role of the problem solver is to not only find solutions to immediate challenges but also to identify opportunities for continuous improvement. By analyzing past experiences and learning from mistakes, the problem solver helps the team grow and evolve, ensuring long-term success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, collaboration is a powerful force driving teams towards success. By understanding and adopting the different team effectiveness models, you can harness the full potential of collaboration.
From the facilitator who promotes effective communication and conflict resolution to the creative thinker who generates innovative ideas and solutions and the problem solver who analyzes challenges and finds solutions, each role is essential in creating a cohesive and high-performing team.





