The streaming music market is booming, with innovative music streaming apps transforming how we consume and discover music. But how do you take a project from concept to reality?
The current business model for media consumption is streaming, such as with Netflix for movies and music streaming services like Spotify or Apple Music. With consumer preferences depending on streaming music rather than owning individual albums, many developers look towards developing streaming services.
The main questions surrounding this initiative are:
- How to start a streaming business music solution and develop your own music streaming app like Spotify?
- How much does it cost to develop the infrastructure?
- What are the streaming platform development tips?
- How do we create a seamless user experience?
This comprehensive post will guide you through the essential steps of launching a music app similar to Spotify, the global titan.
An Introduction to Music Streaming Services
The streaming music industry has experienced a meteoric rise driven by factors such as the widespread availability of high-speed internet, the increasing penetration of smartphones, and the surge in users who prefer to pay for access to millions of licensed music songs rather than own a limited collection. Despite the intense competition, there’s always room for an app that can resonate with a different chord or fill a niche.
But, to succeed in this space, your music streaming solution must incorporate technology to satisfy users and offer something that sets it apart, whether through superior personalization algorithms, a unique user experience, or innovative social features.
Before we go deeper into starting a streaming business for music, understand that the heart of this business is music — the universal language of love, protest, and everything in between.
The challenge is to infuse technology into this art form without weakening its essence.
You must also recognize the importance of innovation. Spotify’s success was not just about providing access to different music genres — it was in how it disrupted the traditional distribution model, reshaping how artists are discovered, how fans engage, and how the industry functions.
Understanding the Market: Recognizing the Music Trends
Before you start with the platform development, a comprehensive understanding of the industry’s current state and trends is important.
The Streaming Market for Music
As we write in our recommended 136 business ideas, where one of them was a music streaming business. The revenue in this industry for 2023 was estimated at $17.7 billion. As of January 2024, there are 90 million paid streaming subscribers for music worldwide. What is more important is that it is expected to grow.
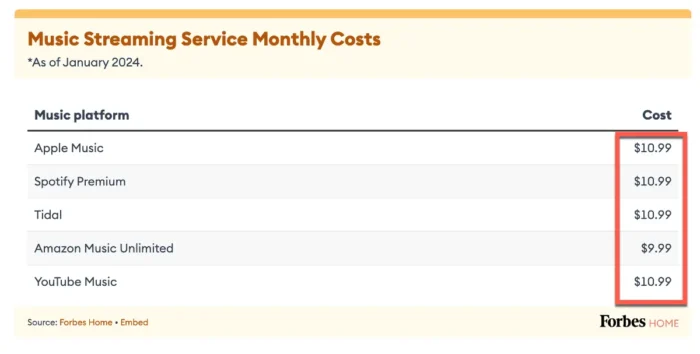
You see that the streaming music industry is generating billions, with a significant chunk shifting from physical sales and downloads. Spotify, Apple, and Amazon Music Unlimited control the market’s share, with others continually shaking for space in this competitive space.
Analyze the Main Players
A deep analysis of various market leaders will help you identify the gaps you could potentially fill. Consider Spotify’s great playlist curation, Apple Music’s seamless integration with other Apple devices, and Amazon’s bundling with Prime membership.
Each of these streaming services has developed its own unique path to success, which your application should respect while finding its distinct identity.
Related: How to be an Entrepreneur in the Music Industry
Key Steps for Starting a Streaming Business Music

Your best initiatives will fall flat without a robust launch strategy.
Conduct Market Research
Market research will guide you to understand user preferences, listening habits, and the most sought-after features that can differentiate your offering.
- Identify your target audience: Clearly define who your target audience is. Differentiate your market segments by demographics, geography, psychographics, and behavioristics.
- Analyze your competitor’s strategies: Study the market leaders and niche players to understand their strengths, weaknesses, offerings, and customer feedback.
- Gather industry insights: Stay up-to-date on the latest industry reports, trend analyses, and forecasts. Resources like IFPI’s Global Music Report can provide valuable data.
- Engage with music listeners: Use surveys, interviews, or focus groups to get direct insights from prospective users.
- Leverage digital analytics: Use digital tools to measure potential customer interaction with music-related content.
- Monitor music consumption patterns: Track how different demographics engage with music, from genre preferences to playlist-building habits, via platforms like Nielsen Music or Chartmetric.
- Keep an eye on technological advances: Investigate how emerging technologies may impact business music streaming experiences, such as the growing use of AI and machine learning algorithms.
- Evaluate legal considerations: Understand the legal landscape of fully licensed music, royalties, and artist compensations to ensure your business model aligns accurately with industry standards.
You can find more details on conducting market research in our market research guide.
Infrastructure Requirements
Music streaming services require an infrastructure for storing the music acquired by the streaming company. Song sizes depend on the quality of the songs being streamed. Apple Music has a typical song quality of 256 kbps, a typical song quality, and the smallest song size for streaming with good sound quality. Other streaming companies have utilized a standard, HiFi, which allows for higher quality and better-sounding audio. HiFi audio also requires more storage space.
Spotify and Apple Music have between 30 and 40 million songs. Songs average around 4 megabytes a piece, multiplied by a typical 30 million songs library, and a streaming company is looking at investing in at least 120 terabytes of storage space, which gets quite expensive. There are also services available where a company can rent server space from other companies rather than invest in building the infrastructure themselves. This may be cheaper than building up a server in-house, but rent is typically monthly or annually.
A single server, however, is unreliable for reaching millions of users. Therefore, to create a seamless experience, a you will need to have a means of quickly and efficiently streaming the stored song data to users’ devices. Spotify uses a system in which data from the main server is cached between other servers and users’ devices to determine if the data already downloaded to one user’s device can be quickly forwarded to another.
Related: How to Download Netflix App on Mac
Content Acquisition – Fully Licensed Music
Moving past the technical details of the infrastructure, a company will also need content in the form of licensed music to populate their server with. Spotify and other streaming services don’t own the content stored on their servers. The songs and rights to the music belong to the record labels and the artists who created the music originally.
Streaming services sign contracts with these entities to gain a period of time when the music can be streamed on their services. These contracts will often have licensing fees associated with them, adding more overhead for the costs to stream content.
Many songs have open contracts, but for an added fee, some streaming services have gained a competitive advantage by securing exclusive contracts for licensed music with some artists. These exclusive offerings are good options to differentiate your streaming service from others and gain a consumer base likely to select your streaming platform for an artist they can only listen to through your service.
As for expected costs for acquiring the licensing fees and exclusive content, popular artists will cost more money than artists who were famous in the past and no longer are. A balance must then be struck between young consumers, who would subscribe to listen to popular artists, and older consumers, who are likely to listen to older music for nostalgic value. The goal, naturally, is to attract more consumers to your platform and retain them.
Performing Rights Organizations
Performing Rights Organizations, often called performance rights organizations or PROs, play a fundamental role in the music industry, particularly for streaming apps.
In essence, PROs are organizations that protect the rights of songwriters and publishers, ensuring they receive fair compensation whenever their music is publicly performed. This includes performances on radio, television, live concerts, and yes, streaming apps.
Whenever a song is streamed, a public performance occurs. Therefore, streaming services need licenses from PROs to legally stream music to their users. The fees paid by these streaming platforms are then distributed among the songwriters and publishers represented by each PRO.
Examples of PROs include the American Society of Composers, Authors and Publishers (ASCAP), Broadcast Music, Inc. (BMI) in the U.S., and the Society of European Stage Authors & Composers (SESAC).
Main Features to Consider

In developing a competitive audio streaming app, it is crucial to incorporate innovative features that cater to the current music audience.
Here’s a rundown of essential functionalities that could set your application on the path to success:
- Personalized custom playlists. Using sophisticated algorithms to suggest music based on individual listening habits, curated custom playlists remain critical for user retention. Spotify’s “Discover Weekly” is a testament to the power of personalization in improving the listening experience.
- High-quality audio streaming. All music listeners prioritize sound quality. So, as seen with Tidal, offering lossless, high-fidelity audio options can distinguish your service for those who want studio-quality sound.
- Social integration. Features like creating and sharing playlists with friends or seeing what others are listening to can transform listening into a social experience. Spotify allows users to connect over music, fostering a sense of community.
- Offline play. The option to download songs and listen offline is non-negotiable for listeners on the go. This feature is convenient and essential in regions with unreliable internet connectivity.
- Music discovery. Helping users uncover new artists or songs is a key differentiator. Apple Music’s human-curation aspect provides listeners with fresh and personalized music recommendations.
- Multi-platform accessibility. Ensuring users can access their music seamlessly across various devices, from smartphones to smart speakers, is fundamental.
- User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX). An intuitive, user-friendly interface for your streaming business music solution ensures that listeners can easily navigate the application. The design should be appealing and functional, removing barriers between users and their next favorite songs.
- Voice control and AI integration. Voice-controlled features for hands-free operation leverage AI to improve user interaction, as seen with Spotify’s voice commands within the application or through smart home devices. AI integration is great for generating a custom playlist through song recommendations. So, AI can help users to create their own playlists easily.
- Exclusive content and releases. Providing exclusive access to own branded mixes and albums or hosting live virtual events can attract users seeking unique experiences.
- Podcasts and extra-media content. As Spotify has successfully done, diversifying the content offering to include podcasts appeals to a broader audience, turning the application into a one-stop shop for audio entertainment.
Each feature can contribute to a music service that meets and exceeds user expectations, encouraging adoption and loyalty.
App Design

By now, the underlying infrastructure for the company has been built, and content has been acquired. The last major component for accessing this content is the user interface. Most users will be listening to music through a smartphone of some kind, so if the budget only allows application development targeted at one device, the smartphone is the one to target.
However, the application should be designed for all platforms possible to maximize a user base. This can be a difficult task because the program would need to offer a similar experience across all platforms while optimizing a user interface designed to give the best possible experience using the united elements of that device’s user interface.
A smartphone offers a small display perfectly suited for the typical view of the album art, play bar, control buttons, volume adjuster, and room for some animations to view lyrics, other songs in an album, and/or a queue list. A tablet and a desktop computer will have a larger screen that will be wasted if the smartphone interface is simply copied and pasted.
In addition to the windows, other UI elements must be considered. Buttons, menus, and interface items designed for touch-based devices should have large enough items to be tapped with fingers, while computers should have buttons designed with a mouse cursor in mind. Most tablets and smartphones only allow a single window to be open, so large buttons are good for those, but for a computer, elements that are as small as possible would be better since users would have the option of having it as a side window to operate beside their other work.
In general, a user should be able to quickly use the play and skip buttons, as those are the most common actions to which a user wants quick access. Other user interface elements are based on features that may be unique to the applications.
Startup Costs

Starting a streaming music platform involves various costs. Here’s a breakdown based on my recent research:
- App Development: The cost of developing a streaming application like Spotify for Android and iOS can range between $45,000 and $250,000. The cost can vary depending on the complexity of the app and the features you want to include.
- Content Acquisition and Licensing: Music streaming services must secure rights holders’ licenses. Costs can vary depending on the size of your user base, the territories you operate in, and the specific agreements you negotiate with rights holders. Artists and music record companies charge for the content. This cost will depend on your agreements with these entities.
- Hosting and Maintenance: Ongoing costs for hosting and maintaining the app can vary widely, but you should budget for these expenses.
- Marketing and Promotion: These costs can also vary significantly, but they’re crucial for attracting and retaining users.
Revenue Model

Your app’s revenue model is important for your success because without the right monetization, your new business can not pay the bills, and as we already discussed, they will not be low.
Subscription Model
This is one of the most common models of streaming services like Spotify and Apple Music use. Users pay a monthly or yearly fee for unlimited access to the platform’s entire music library. It often includes perks like ad-free listening, offline downloads, and high-quality audio.
Freemium Model
This model offers basic features for free but requires payment for advanced features or ad-free listening. Spotify uses this model alongside its subscription model, allowing users to listen for free with commercial interruptions and limited skips.
Ad-Supported Model
Do not undervalue the advertising dollar. In-app ads, branded playlists, and exclusive audio ad slots can be the golden ticket for revenue.
In this model, the service is free for users, but they must listen to advertisements between songs. The revenue comes from advertisers who pay to have their ads played on the platform. An example is the free version of Spotify.
Pay Per Stream Model
This model charges users for each song they stream. While not commonly used for music, it’s prevalent in movie and TV streaming services.
Direct Sales Model
You can allow artists to sell their music directly to fans through your application. For example, you can allow artists to set their own prices and offer users the option to pay more. You will get a fee for each purchase.
Data Monetization Model
Streaming services can sell valuable data insights to record labels, artists, and advertisers by analyzing user behavior and preferences.
Music for Business Use
There are many companies that need to have music for business use, or music for commercial use for the purpose of their business operations. This music for business can be one of your specific niches you can target with your own music system for commercial use.
So, you can also offer music for business use, which means you will provide licensed music that can be used in commercial areas such as retail stores, restaurants, and offices. It can be one of your licensed background music.
You can also work with professional music designers to design specific music that can be used as music for business in physical locations or online like background music highly required for online videos.
So, this revenue model will require you to create your own branded mixes from the world’s largest library, fully licensed, or your own music for business use. Ensure you have an easy-to-use platform that allows your business users to fine-tune their business’s music through your service.
Marketing Your New Business

Social Media
Leverage the power of social media platforms to create a buzz, build communities, and disseminate content that resonates with music lovers.
Influencer Marketing
Engage with influencers, artists, and tastemakers who can lend their credibility to your brand and extend your reach to their dedicated followers.
App Store SEO
Optimize your app’s store presence with strategic keywords, appealing visuals, and a compelling description to ensure your target audience can find you among the cacophony of competitors.
General Tips
Aside from the unique experience of listening to the music and content in the application , the unique features that bring a personal touch to a music library are also important. The way users can organize their music and find new music that they would be interested in is critical not just for retaining users to your service but also for attracting contracts with artists who have a better chance of being heard through your platform.
Spotify has a strong social aspect that allows users to share songs, and most streaming services have some type of algorithm designed for curating new playlists and suggesting new songs. That algorithm gives users a feeling of a personal approach that fascinates them.
Summary
Above is a brief overview of the main components required for starting a streaming service. It is important to note that all of them must be done well. Content must be chosen wisely to please a wide audience. The infrastructure must be designed to support a large library of content to offer various song options. This infrastructure must also be designed to quickly and seamlessly transmit the audio files to users as they listen to their content; they must never notice a pause in their experience, or they will decide to seek better service.
Also, you must select the right revenue model, like subscription, or selling background music for business, or some combination of explained models.
Lastly, the look of the application they use to play and access their content must be intuitive and offer a visual, exciting interface that makes users want to listen to music with your service. These are the ingredients of successful Spotify-like streaming application development.





