In a world where businesses constantly compete for customers’ attention and loyalty, understanding the processes that create value for your products or services is crucial. Value chain analysis is a strategic tool that allows you to examine your business’s internal activities and identify areas for improvement. With this knowledge, you can gain a competitive advantage and achieve long-term success.
But how exactly does value chain analysis work, and can you use this tool to achieve great competitive advantage?
📖 Key Takeaways
- Value chain analysis is a strategic tool used to identify areas of competitive advantage and maximize customer value.
- It consists of two components (primary and support activities), which, when assessed, provide insight into potential improvements.
- Tools, templates & software solutions can help businesses optimize their operations for long-term success.
Understanding Value Chain Analysis
Value chain analysis is a powerful method to assess your company’s internal activities and pinpoint areas for enhancement, ultimately achieving a competitive advantage. Developed by Harvard Business School Professor Michael Porter, this concept focuses on examining the primary and secondary activities a firm performs, how they are performed, and how they interact to analyze the sources of competitiveness.
Related: 31 Startup KPIs and Metrics to Measure with Examples
Value chain analysis enables you to compete more effectively, establishing an efficient value chain that generates maximum customer value with minimal costs.
Definition of Value Chain Analysis
Value chain analysis is a strategic tool that evaluates a company’s internal activities, identifies areas for improvement, and acquires a competitive edge. Its purpose is to assess processes and practices to:
- differentiate your company from competitors
- offer more value to your customers
- boost revenue and profits for your company, and
- improve operational efficiency in your business activities.
Michael Porter from the Harvard Business School was the first to use the term “value chain” in his book Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance from 1985. It analyzes the entire production system, from raw materials purchase to final delivery. Porter aimed to analyze a company’s activities to identify its primary and support activities that create value for the organization.
This tool, which involves deconstructing a company’s operations into its key components, assists your company in understanding the costs and values associated with each activity. This understanding lets you identify the most critical improvement areas, leading to cost savings and a more efficient production process.
Related: How to Add Value to Your Products and Services
Importance of This Analysis
The importance of this analysis lies in its ability to help your company improve and simplify processes, reduce costs, and increase customer value. You can gain a competitive edge over your competitors by exposing areas where you can improve your operations based on this concept related to value. This systematic approach to understanding the interactions between primary and support activities enables you to identify positive or negative practices and processes that differentiate you from your competitors.
Through value chain analysis, you can achieve a cost advantage by reducing production costs or a differentiation advantage by offering customers unique and valuable products or services. Either way, the ultimate goal is to generate or reinforce your business’s competitive advantage. Concentrating on these key areas allows you to optimize your operations, crafting a value chain that delivers the highest value at the lowest possible cost.
The Components of Value Chain Analysis
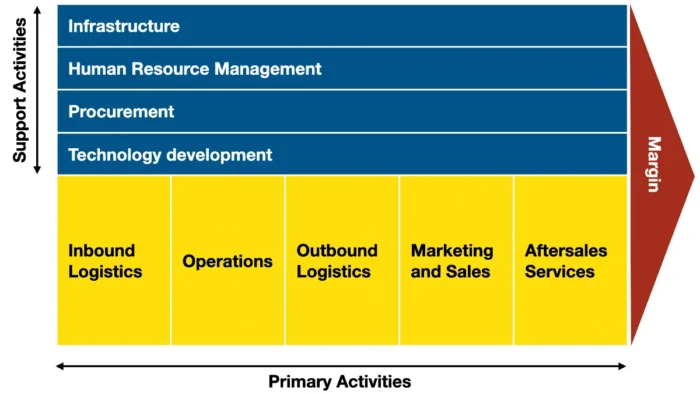
To effectively conduct a value chain analysis, it’s essential to understand its two main components: primary and support activities. Primary activities are the core functions that are directly involved in creating a product or service. In contrast, support activities are the indirect ones that help primary activities do the job and become more efficient.
Assessing these components, you can easily find areas that require improvements to achieve a higher level of potential competitive advantages.
Primary Activities
Primary activities refer to the core functions of a company that are directly involved in producing and distributing their product.
Each of these activities plays an essential role in ensuring smooth functioning. Properly managing primary activities can be the source of your business’s cost advantage, allowing you to provide a product or service with better quality and at a lower cost than your competitors.
Porter’s value chain model consists of five primary activities:
Inbound logistics
Inbound logistics is an essential part of the supply chain process that involves moving, storing, and delivering goods coming into a business. This could range from raw materials from suppliers to goods returned by customers. For example, a furniture manufacturing company relies on various raw materials such as wood, metal, and fabric. These materials, procured from different suppliers, form the basis of the inbound logistics process.
Operations
Operations in a business context refer to a company’s day-to-day activities to produce goods or provide services to customers. This involves turning resources such as labor, capital, and raw materials into outputs like products or services that are of value to customers.
Outbound logistics
Outbound logistics refers to the process of storing, transporting, and distributing goods to end customers. It’s an integral part of a company’s operations, as it ensures that products reach their intended destination promptly and efficiently. For example, consider outbound logistics from an online retailer like Amazon. Once you place an order, Amazon retrieves the product from its warehouse, packages it, and arranges for its delivery. All these activities are part of outbound logistics.
Marketing and sales
Marketing and sales activities are those that make customers aware of products and services, generate customers to purchase them, and facilitate their purchase. These activities play a crucial role in creating customer value and, thus, contribute significantly to the overall value chain.
Aftersales services
Aftersales services, or post-sales services, involve all business activities that take place after a product has been sold to ensure customer satisfaction and encourage long-lasting relationships. These business activities can significantly improve the overall value provided to customers.
In the context of value chain analysis, primary activities are crucial because they directly contribute to creating and delivering the product or service (value for the customers). They are essential for your business to gain a competitive advantage, ultimately sustaining superior performance.
Optimizing these activities can lead your company to significant cost savings, higher customer value, and a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Related: 4 Steps Business Idea Generation Process in Entrepreneurship
Support Activities
On the other hand, support activities encompass the indirect functions that facilitate the optimization of primary activities. Although they may not directly contribute to creating the product or service, support activities are vital in making primary activities more efficient and cost-effective.
Porter’s model includes four support activities:
- Infrastructure. Infrastructure refers to the organizational structure, facilities, systems, and resources that form the backbone of any company. This includes everything from physical assets like buildings and equipment to operational processes and the organizational culture.
- Human resource management (HRM). HRM involves managing people within an organization to bring out their best and align their contributions with the company’s goals. This includes everything from recruitment, training, and development to compensation, benefits, performance management, and maintaining a positive work environment.
- Procurement. Procurement involves everything from identifying and evaluating potential suppliers, negotiating contracts, and establishing payment terms to ensuring timely delivery of high-quality inputs.
- Technology development (some authors also refer to research and development). Technology development covers all the technological advancements and innovations a company uses to produce and improve its products or services, improve operational efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage. This could involve everything from research and development (R&D), equipment, hardware, and software systems to digital platforms, data analytics, and so on.
Upon evaluating support activities during this analysis, you can find improvement opportunities in areas like human resource management, technological development, and procurement processes. By optimizing these activities, your company can enhance the efficiency of its primary activities and ultimately deliver more value to its customers at a lower cost.
Value Chain Analysis Example – Define Primary and Secondary Activities
Let’s utilize a value chain analysis example for the e-commerce giant Amazon to illustrate this analysis.
Primary Activities
Primary activities in Amazon’s value chain are the following:
- Inbound Logistics: Amazon sources millions of products from suppliers around the world. They have established efficient processes and systems for receiving, storing, and managing inventory in their numerous warehouses globally.
- Operations: Amazon operates an extensive network of fulfillment centers where products are picked, packed, and shipped based on customer orders. They also offer services like Amazon Web Services, Prime Video, and Kindle, among others.
- Outbound Logistics: This is a critical activity for Amazon. Their advanced logistics network ensures fast and reliable delivery, often within one or two days for Amazon Prime members. They use a combination of courier services and their own delivery network.
- Marketing and Sales: Amazon uses targeted online marketing strategies such as personalized recommendations, email promotions, and paid advertising. They also have an extensive customer review system that influences sales.
- Service: Amazon flatters itself on customer-centricity. Their service includes easy returns, comprehensive customer support, and the Amazon Prime program with benefits like fast shipping and access to digital content.
Support Activities
On the other side, supportive activities in Amazon’s value chain are the following:
- Firm Infrastructure: Amazon’s infrastructure includes its corporate headquarters, regional offices, data centers, and fulfillment centers. They also have robust IT systems to handle e-commerce transactions, data management, and cybersecurity.
- Human Resource Management: Amazon employs over a million people worldwide. Their HR practices focus on recruitment, training, and retention. They also invest in employee development and offer competitive compensation packages.
- Technology Development: Technology is at the core of Amazon’s operations. From their e-commerce platform to cloud services to AI and machine learning used in their recommendation systems, technology drives their business.
- Procurement: Amazon procures a wide variety of goods from suppliers globally. They focus on securing the best prices, maintaining quality, and ensuring reliable supply chains.
This analysis reveals how each activity contributes to its overall value proposition – vast selection, competitive prices, and convenience. This understanding helps Amazon continuously improve customer experience, simplify operations, and maintain a competitive advantage in the e-commerce market.
Porter’s Value Chain Framework
Michael Porter’s value chain framework is a widely used tool for conducting value chain analysis, offering a comprehensive and systematic approach to evaluating your company’s internal activities. Employing Porter’s framework enables you to dig deeper into your value creation chain and implement changes that can amplify efficiency and profitability.
Utilizing Porter’s value chain model, you can systematically analyze each activity and measure its contribution to the overall product or service value. This approach enables you to:
- Identify areas for improvement
- Identify potential competitive advantages
- Increase efficiency and effectiveness
- Increase profitability
It is important to break down each company activity and determine how it relates to customer satisfaction and service quality. This approach helps you to identify where value is added for customers and how each activity affects the overall performance of your company.
Advantages of Using Porter’s Framework
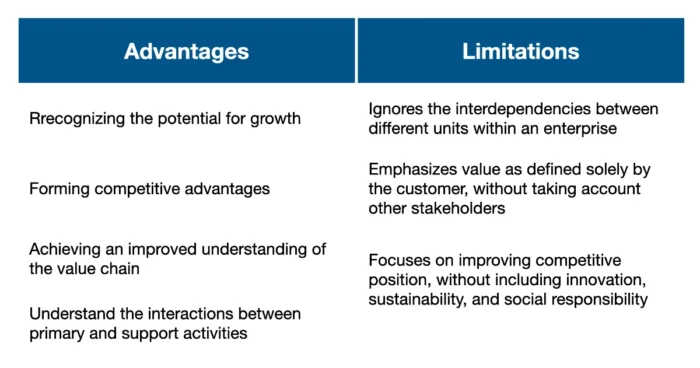
Using Porter’s framework for analysis offers several advantages, such as recognizing the potential for growth, forming competitive advantages, and achieving an improved understanding of the value chain. The framework’s systematic approach enables you to identify and assess the activities that generate value, analyze the costs associated with each activity, and compare performance against competitors.
Moreover, Porter’s framework can help you better understand the interactions between primary and support activities, allowing you to make more informed decisions and effectively allocate resources. By employing this comprehensive and systematic method, you can optimize your value chain and pave the way for long-term success amidst marketplace competition.
Limitations of the Framework
Several limitations to this approach must be taken into consideration.
Firstly, the framework focuses on the business unit as the unit of analysis. While this can be useful for identifying areas of improvement within a specific business unit, it ignores the interdependencies between different units within an enterprise. To address this, a more holistic approach is required, which considers an enterprise’s entire value chain.
Secondly, this analysis emphasizes value as defined solely by the customer. While this is important, it ignores that the company must also create value for other stakeholders, including shareholders, employees, and society. A more comprehensive approach would consider the needs of all stakeholders and seek to create value for everyone involved.
Thirdly, value chain analysis focuses on improving competitive position, which is certainly important. However, it is only one component of the company’s transformation efforts. To truly transform a company, it is important to consider a broader range of factors, including innovation, sustainability, and social responsibility.
Steps to Conducting a Value Chain Analysis
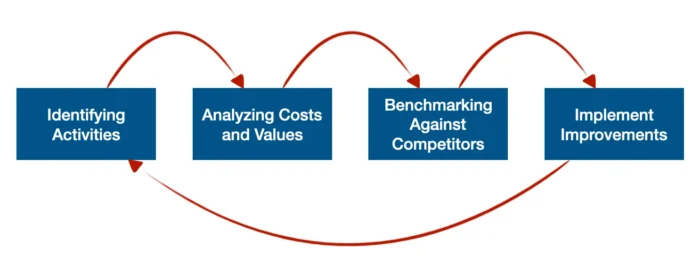
Conducting this analysis involves a systematic process that can be broken down into several steps, from identifying activities to implementing improvements. Following these steps can provide you with valuable insights into your operations and highlight areas for improvement and optimization.
1. Identifying Activities
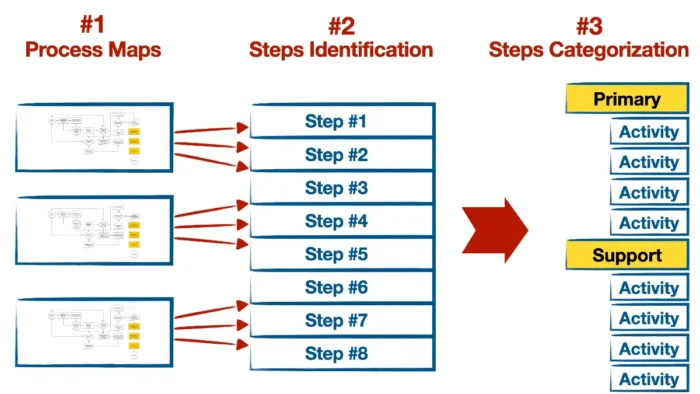
The first step in value chain analysis is identifying all primary and supportive activities involved in producing and delivering a product or service. This involves examining each aspect of your business, from procurement and production to marketing and sales, and understanding how these activities contribute to the overall value of the product or service.
Simply, you need to respond to the question of what your company is doing to make your customers happy. So, you can start by listing everything your business must do to satisfy the customers. But you can not start by listing only the activities. You must start with the processes and then, for each process, list the most critical activities. Here are some steps you can take:
- Process maps. Start by mapping out all the processes in your company. To achieve this, you must talk to employees, observe the production floor, and review the whole process documentation.
- Identify each step in all processes. Break down each process into its steps. For example, producing automotive parts could include everything from receiving the raw materials to assembling the produced parts to shipping the finished product.
- Categorize each step. Once you have a detailed list of every step in your production process, start categorizing them into primary activities and secondary activities.
Remember that, at this stage, you must encourage cross-collaboration during the identification of value chain activities if you want to expedite the process and enhance the quality of work. By involving all relevant departments and stakeholders in the process, you can understand their value chain comprehensively and ensure that no essential activities are overlooked.
2. Analyzing Costs and Values
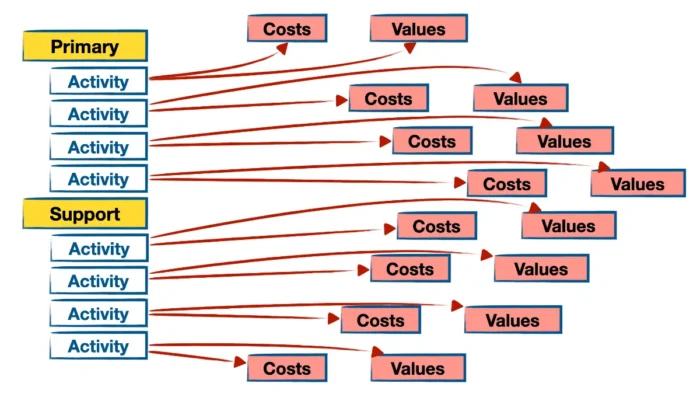
Once you have identified the activities, the next step is to analyze the costs and values associated with each activity. This involves computing the cost of all activities contributing to the company’s products and assessing how those activities produce value for customers and stakeholders.
Understanding each activity’s costs and values will help you identify areas for improvement and potential competitive advantages. Analyzing costs and values can be a complex and time-consuming process, but it is a crucial step in value chain analysis.
3. Benchmarking Against Competitors
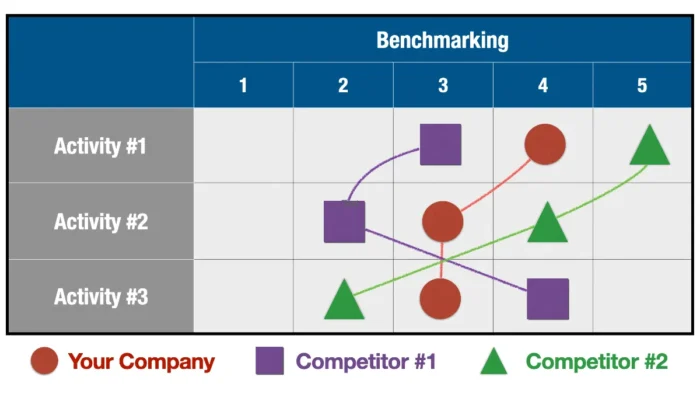
Comparing your value-creation chain to those of your competitors is an essential step in the analysis process, as it can help identify best practices and areas where your business can gain a competitive edge. This process, known as benchmarking, involves comparing your company to competitors using relevant metrics and examining differences in performance. Understanding how your value chain stacks up against your competitors can help identify improvement areas and opportunities to gain a market competitive advantage.
Benchmarking can be a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes, as it provides insights into industry best practices and highlights areas where your company may be lagging behind. By regularly benchmarking your value chain against competitors, you can stay ahead of industry trends and ensure that your business remains competitive in the long run.
4. Implement Improvements
Once you have identified areas for improvement, you can prioritize and implement changes to optimize your value chain. This may involve reallocating resources, investing in new technology, or updating processes to increase efficiency and reduce costs.
Here is an example where I have worked as a consultant to improve processes through conducting value chain analysis. As you can see in the image below, we have played with different layouts inside the plant to ensure that the output will have the highest possible value while keeping the costs at the lowest possible level.

Implementing improvements can be challenging because this often requires significant time and resources. On the other side, there will always be some resistance to change. However, you must put the focus on the most impactful changes and regularly monitor progress. In such a way, you can ensure that you are making the most of your value chain analysis efforts.
You and your team must continually reassess and update your company’s value-creation chain over time because market conditions and industry trends change. Maintaining agility and adapting to new challenges allows you to sustain a competitive edge and secure your long-term success.
Related: The Team Effectiveness and Different Roles in Teams That Win
Tools and Templates for Value Chain Analysis

As value chain analysis can be a complex and time-consuming process, you can benefit from using various tools and templates available to help simplify the analysis and make it more effective. These resources can range from software solutions that automate data collection and analysis to templates and frameworks that assist in visualizing and organizing the value chain.
Utilizing these tools and templates can expedite the identification of improvement areas and cost-saving opportunities for your business.
Software Solutions
Software solutions like NetSuite can help you facilitate your analysis by providing real-time data and insights, automated analysis, and the ability to compare performance with competitors. These tools offer a range of features that can assist you in identifying areas for improvement, prioritizing changes, and monitoring progress over time.

Leveraging technology to automate and simplify the value chain analysis process can result in time and resource savings for businesses while also enhancing their understanding of their operations.
Templates and Frameworks
Templates and frameworks like Porter’s model can help you visualize and organize your value chain activities to improve and optimize your processes. By providing a structured approach to the analysis process, templates and frameworks can assist you in:
- Identifying areas for improvement
- Prioritizing changes that will have the most significant impact on their operations
- Better understanding of the interactions between primary and supportive activities
- Making more informed decisions
- Effectively allocating resources
Utilizing raw materials effectively can be valuable for businesses looking to optimize their value chain and improve overall efficiency.
These resources provide customizable templates and frameworks that can be tailored to the unique needs of individual businesses, making it easier for them to conduct a comprehensive value chain analysis and identify areas for improvement.

Overcoming Challenges in Value Chain Analysis
Conducting this analysis can have various challenges, such as collecting data, identifying tasks or activities within the value chain, and measuring the impact of improvements.
To overcome these challenges, you should:

- Prioritize customer needs,
- Devise flexible distribution plans,
- Foster supplier relationships,
- Leverage technology to automate data collection and analysis,
- Break down the value chain into achievable objectives,
- Recognize the complexity and diversity of the value chain,
- Reserve adequate time for value chain examination and
- Utilize metrics to assess the effect of value chain enhancements.
Addressing these challenges and proactively approaching them with the analysis enables you to optimize operations, establish a more efficient and competitive value chain, and ultimately secure long-term market success.
Summary
Value chain analysis is a powerful strategic tool that allows you to examine your company’s internal activities and identify areas for improvement, ultimately achieving a competitive advantage. By understanding the value chain components, employing Porter’s framework, and following a systematic process, you can gain valuable insights into your operations and optimize your value chain.
By overcoming challenges and continually reassessing their value chain, businesses can maintain a competitive edge and ensure long-term market success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Value chain analysis is a process you can use to identify and evaluate the efficiency of your business’s primary and secondary activities, from product design to customer delivery. It helps you uncover opportunities for improvement that can increase profits and provide a competitive advantage. By understanding the value chain, you can identify areas where you can reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer service. You can also identify areas where you can add value to your products or services by offering additional features.
Value chain analysis involves five steps: identifying primary and support activities, listing the value and cost of each activity, researching competitors’ value chains and customer values to make benchmarking, and implementing improvements.
Value chain analysis involves primary activities, which are the core functions directly involved in creating a product or service, like inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, sales and marketing, and after-sale services. On the other hand, supportive activities are the indirect functions that enable primary activities to become more efficient, like infrastructure, human resource management, procurement, and technology development.
Businesses can successfully overcome challenges in value chain analysis by prioritizing customer needs, developing flexible distribution plans, promoting supplier relationships, leveraging technology, and utilizing metrics to assess improvement.
Value chain analysis can be made easier with the help of various tools and templates such as NetSuite, Creately, Visual Paradigm, Miro, and EdrawMax.





